Book Notes: Technology’s Child
Strategies for Parents in the Digital Age
By Dr. Katie Davis
This book was an especially meaningful read as I got to connect with Dr. Davis (a fellow Eph!) at the Kids & Screens Conference in July 2025.
Concepts
Social Contingency
Linear vs Web Thinking (Universal Design for Learning)
Thought Disorders
Circumstantiality: is when an individual speaks in a circular, “roundabout” manner. They might fall into tangents about unrelated topics before eventually returning to the focus of their statement or the proposed question. Circumstantial thought processes can be challenging for outsiders to understand and follow.
Thought blocking
Distractible Speech: loses their train of thought. They may become distracted by another thought or external distraction, even in the middle of a sentence. Individuals experience confused thoughts that jump from topic to topic, and those listening may struggle to comprehend their story or conversation.
Paraphasic error: constant word mispronunciation or slips of the tongue
Takeaways from Technology’s Child: Themes and Actionable Next Steps
Notes
2 EARLY CHILDHOOD: LEARNING SELF-CONTROL IN A TECH-SATURATED WORLD 19
3 THE DIGITAL FEATURES OF EARLY LITERACY DEVELOPMENT 43
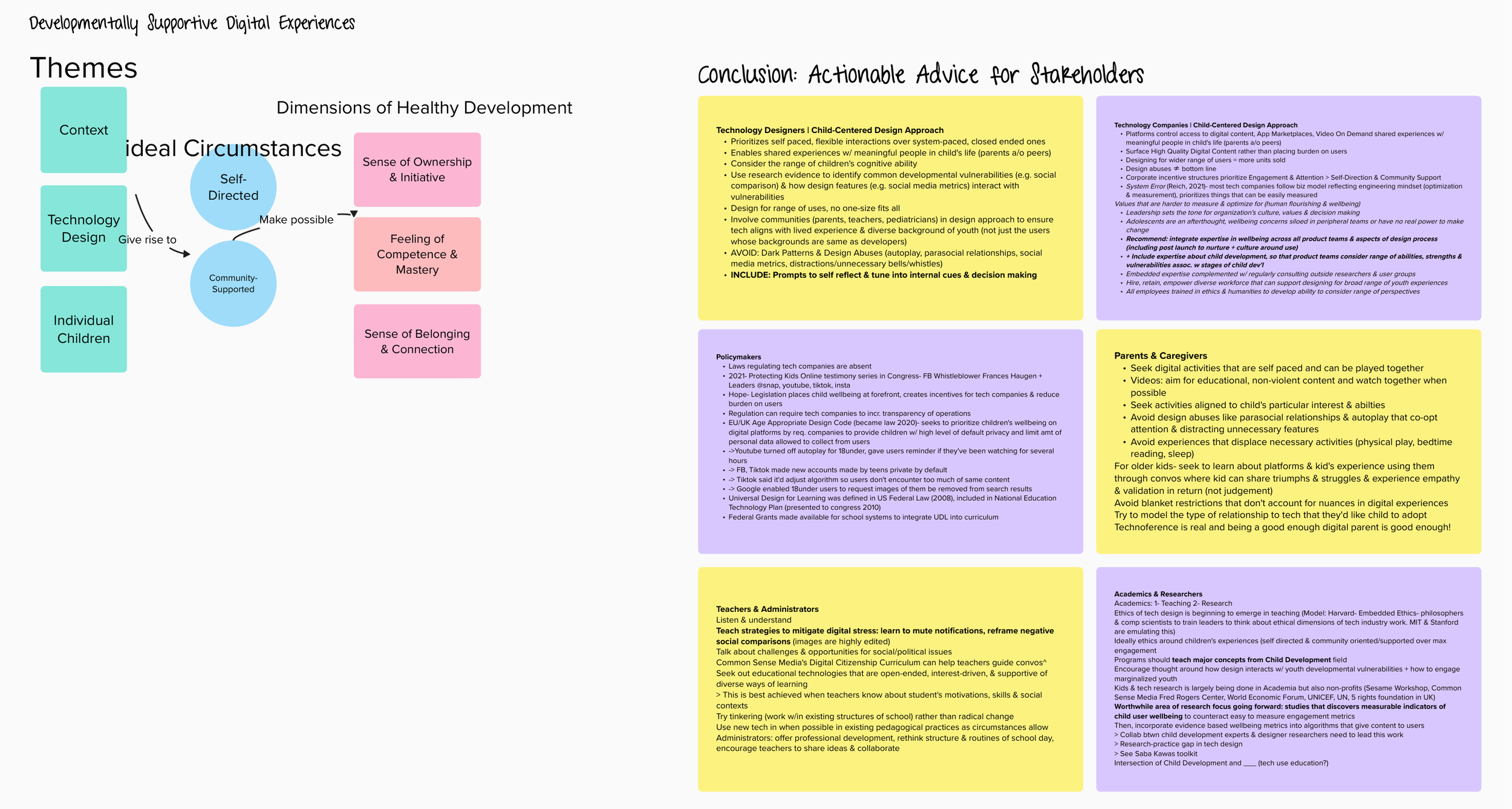
Design for children’s self-directed, community-supported digital experiences
– Feeling out of control ≠ feeling self directed (ownership, self efficacy over tech interactions)
Can’t say lost agency– we have agency
Design abuses: Lures
– Stopping these is in the disinterest of tech companies
– Child must dictate pace of the interaction
How can tech support children’s executive function development, improvement and sustainment?VR and developmental functionality
Milestones – executive function & early literacy development
– Play for self regulation & vocabulary development
Affordances of video games:
– Low cost of failure + immediate feedback
– Optimal balance between challenge & frustration
– Social interaction
Designers should prioritize: Developmentally supportive digital experiences: self-directed pace + community-supported experiences
Feeling of progress & mastery > the need to keep playing
Giving kids opportunities to involve their families in game play
— when do these lead to self directed & community supported experiences? (Key features of developmentally supportive digital experiences)
+ Generate feelings of Personal progress and even mastery
Model school after gameplay?
Same affordances make video games high engagement and feel less voluntary
4 LOOKING FOR “LOOSE PARTS” IN CHILDREN’S DIGITAL PLAY 69
5 THE “CURSE OF THE FAMILIAR” AND ITS IMPACT ON LEARNING 95
– Interest centered learning design
– Kids team UW- 8-11 y/o design partners
– variation is the rule when it comes to the way children learn. Todays learning tech is good at handling individual variation
6 TWEENS: A TIME OF TRANSITIONS AND TENSIONS 125
– During adolescence, parts of the brain related to emotions dev’l faster than those related to decision-making and self regulation.
– Digital Stress & Anxiety: Permanence, publicness, quantifiability = sign of friendship & affiliations
– Friend groups feel extremely consequential/weighty, plus heightened emotional reactivity
– Tweens experience more fluctuations in self-esteem than younger children & older adolescents
– Weinstein, James: public (posts) vs inner circle (group chat) stress– public exclusion, being left on read [Peer-related tensions]
– Snapchat’s ephemerality makes content feel less weighty/consequential
– Bullying= 1) repeated 2) willful 3) causes harm 4) involves power imbalance
– Those at top of popularity hierarchy are those whose appearance, skills, and behavior align most closely w/ the values of the surrounding social & cultural context.
– Tweens use membership in cliques to define their sense of identity
– Behavior that flouts group norms threatens the identity of the clique-> bullying to put tween in line or banish you
– Who gets to be popular or bullied depends largely on structures/social/cultural context surrounding young people
– Stress from FOMO, approval anxiety, increases (-)mental health outcomes
– Community supported children are better equipped to manage digital stress
7 ADOLESCENCE: THE “WHO AM I?” YEARS 153
Teens: 13-17
– Massive neurobiological changes, vulnerability and potential
– Experience well-being and develop/discover identity
– Struggles to achieve self directed digital experiences
– Encourages social comparison
– Positive feedback seeking for identity development
8 THE ONLINE AGENCY OF EMERGING ADULTS 181
Solutioning: a device built with kids in mind (Apple Kids)
WHO definition of gaming disorder
Goal:
Promote Self efficacy
Self-directed digital experience
Ownership of tech interactions
Can’t say lost agency– we have agency
Design abuses
Lures
Stopping these is in the disinterest of tech companies
child must dictate pace of the interaction
Design for children’s self-directed, community-supported digital experiences
How can tech support children’s executive function development, improvement and sustainment?
VR and developmental functionality
Milestones – executive function & early literacy development
Play for self regulation & vocabulary development
Video games core feature is interactivity
Affordances of video games:
Low cost of failure + immediate feedback
Optimal balance between challenge & frustration
Social interaction
Designers should prioritize:
Developmentally supportive digital experiences: self-directed pace + community-supported experiences
Feeling of progress & mastery > the need to keep playing
Giving kids opportunities to involve their families in game play
— when do these lead to self directed & community supported experiences? (Key features of developmentally supportive digital experiences)
Generate feelings of Personal progress and even mastery
Model school after gameplay?
Same affordances make video games high engagement and feel less voluntary
Resources
Universal Design for Learning guidelines: https://udlguidelines.cast.org/
Digital Youth Lab Homepage https://digitalyouth.ischool.uw.edu/
Common Sense Media Digital Citizenship curriculum Digital Citizenship
Saba Kawa’s Interaction Design & Children Designer’s Toolkit https://ischool.uw.edu/capstone/projects/2022/interaction-design-children-designers-toolkit
Questions
What specific factors drive the effect of SES on success?
Access- quiet place to study, tech
Savviness- affluent families know how tech use will connect to future careers and success
Thoughts
Study cognitive psychology and apply to software development/software design
App that develops strong communication skills
So you have circumstantial thinking. 💭 What to do?
Cognitive behavioral app?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5464106/
https://www.choosingtherapy.com/thought-disorder/
mental health condition -> disruption of speech